Types of Recovered Sulfur and Their Applications
Recovered sulfur, derived from oil refining, natural gas processing, and metal extraction, plays a crucial role in the chemical and agricultural industries.
It is used in the production of fertilizers and sulfuric acid and helps reduce environmental pollution by being reintegrated into the production cycle. Utilizing recovered sulfur decreases dependence on raw materials and lowers production costs.
This process also contributes to industrial sustainability and the preservation of natural resources.
Sulfur Recovered from Oil and Gas Industry
Recovered sulfur from the oil and gas industry is obtained as a byproduct from the purification and processing of acidic gases.
This type of sulfur is valuable due to its specific properties and is recycled in the oil and gas sector, contributing to the reduction of environmental pollutants.
Techniques and Methods
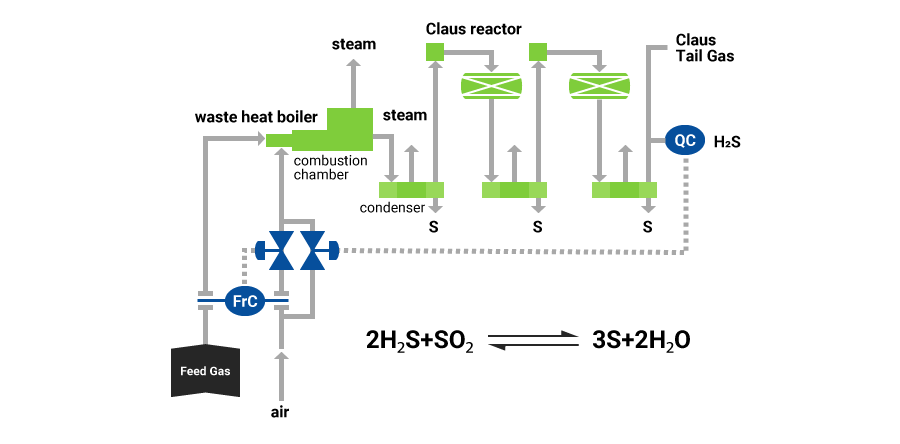
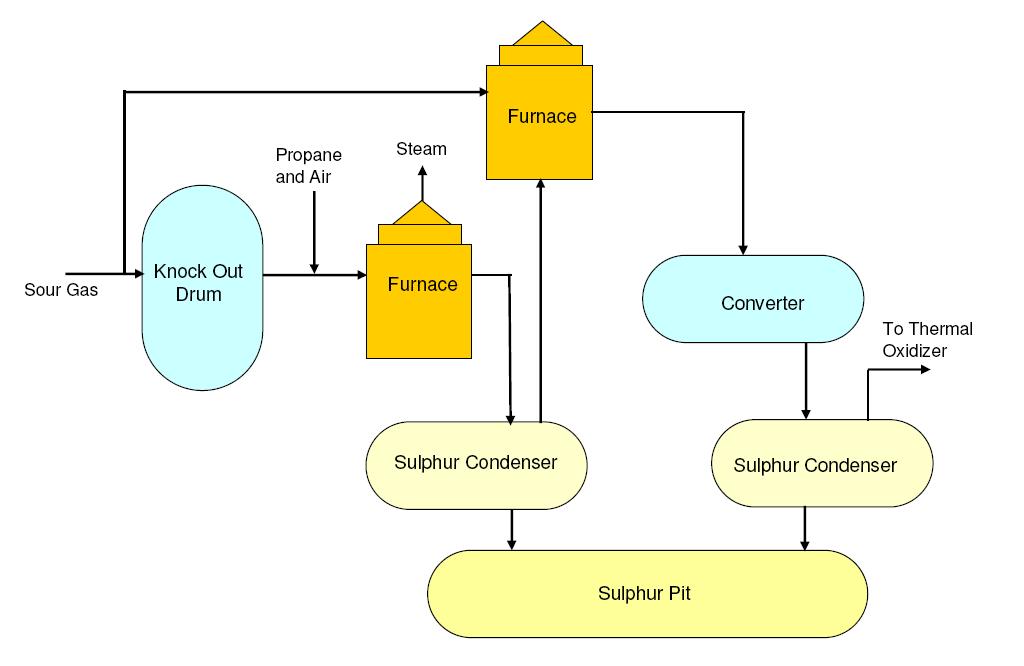
In the oil and gas industry, recovered sulfur is primarily obtained through two main methods: the Claus process and the Sulfur Recovery Unit (SRU).
The Claus process involves converting hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) into elemental sulfur by reacting it with oxygen in catalytic reactors. The SRU, which includes various processes such as Claus, is used to collect and recover sulfur from industrial gases. Newer technologies like the SuperClaus process and Modified Claus process further enhance sulfur recovery efficiency and rates.
Industrial Uses and Benefits
Sulfur reclaimed from the oil and gas industry is primarily used in the production of sulfuric acid, which is essential for manufacturing agricultural fertilizers and industrial chemicals.
This sulfur also enhances soil quality and crop yields through its use in sulfate-based fertilizers. Additionally, it is utilized in metallurgical processes for refining metals.
The recovery of sulfur from oil and gas helps reduce industrial waste and lowers emissions of harmful gases such as sulfur dioxide, contributing to environmental protection and improved air quality.
Sulfur Recovered from Coal
Sulfur reclaimed from coal is a byproduct of the coal carbonization and purification processes.
This sulfur, primarily in the form of hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide, is used in various industries, including the production of sulfuric acid and chemical fertilizers.
Techniques and Methods
The recovery of sulfur from coal typically involves several key techniques. One common method is the Claus process, which converts hydrogen sulfide, a byproduct of coal gasification, into elemental sulfur.
Fluidized bed combustion is another approach, where coal is burned in a bed of particles, and sulfur is captured using lime-based sorbents.
Additionally, pre-combustion desulfurization can be employed to remove sulfur compounds from coal before combustion, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing emissions. These techniques not only help in recovering sulfur but also contribute to mitigating environmental impacts.
Industrial Uses and Benefits
recovered sulfur from coal is primarily utilized in the production of sulfuric acid and chemical fertilizers, which are crucial for agricultural and industrial applications.
Additionally, it plays a significant role in water treatment processes and the manufacture of various other chemicals. Its applications are particularly valuable in environmental management and the production of essential industrial materials.
Sulfur Recovered from Metallurgical Processes
Sulfur recovered from metallurgical processes is a byproduct of metal refining, mainly from gases released during metal extraction.
It is essential for producing sulfuric acid and other industrial chemicals, and helps reduce environmental impacts from metal production.
Techniques and Methods
Sulfur recovery from metallurgical processes employs several advanced methods. The wet gas sulfuric acid (WSA) process converts sulfur dioxide in flue gases into sulfuric acid using a catalyst.
The Claus process recovers sulfur from hydrogen sulfide by converting it into elemental sulfur.
Additionally, ammonia-based scrubbing captures sulfur dioxide from gases and converts it into sulfuric acid. Essential equipment includes catalytic reactors, gas scrubbing units, and distillation and absorption systems for processing and converting sulfur-containing gases into valuable products. These techniques are crucial for reducing emissions and reclaiming sulfur for industrial applications.
Industrial Uses and Benefits
Sulfur reclaimed from metallurgical processes is primarily used in the production of sulfuric acid, essential for various industrial applications. This sulfur is also utilized in metal refining processes, enhancing the quality and efficiency of metal extraction.
Unlike sulfur recovered from coal or oil and gas, which is mainly used in fertilizer production and pollution control, metallurgical sulfur is specifically focused on improving metal processing and industrial applications.
Sulfur Recovered from Waste and Industrial By-Products
Sulfur recovered from waste and industrial by-products is derived from various manufacturing and waste treatment processes.
This sulfur, often recovered from chemical residues or by-products, is repurposed for producing sulfuric acid and other industrial chemicals. Its use helps to minimize environmental impact and enhances resource efficiency by recycling sulfur from otherwise discarded materials.
Techniques and Methods
Sulfur recovery from waste and industrial by-products involves techniques such as chemical absorption, where sulfur is extracted from industrial gases using chemical agents, and chemical conversion, where sulfur is recovered from chemical residues.
Additionally, biochemical processes, utilizing microorganisms for sulfur extraction, and thermal processes, where sulfur is liberated from waste materials through high-temperature treatment, are employed. These methods enhance sulfur recovery from indirect sources and help reduce industrial waste.
Industrial Uses and Benefits
Sulfur recovered from waste and industrial by-products is particularly used in producing sulfuric acid and specialized chemicals such as metal sulfates, ammonium sulfides, and additives.
This type of sulfur is applied in chemical waste treatment and management processes, helping to reduce production costs and minimize environmental impacts from discarded materials.
Unlike sulfur recovered from oil, coal, and metal industries—which focuses more on fertilizer production and metal processing—sulfur recovered from industrial waste is concentrated on recycling residual materials and optimizing industrial processes.
The recovery of sulfur from diverse sources such as the oil and gas industry, coal, metallurgical processes, and industrial waste plays a crucial role in resource management and environmental impact reduction.
Sulfur reclaimed, available in forms such as elemental sulfur, sulfuric acid, and specialized chemical compounds, is widely used across chemical and agricultural industries.
Optimal use of recovered sulfur not only reduces reliance on raw materials and production costs but also promotes industrial sustainability and natural resource conservation. With advancements in recovery technologies and growing environmental awareness, the use of recovered sulfur is expected to expand, significantly enhancing industrial processes and mitigating pollution in the future.
other posts:
get more and free information about products and services automatically in email: